4.1: Panel Data and Fixed Effects
ECON 480 · Econometrics · Fall 2019
Ryan Safner
Assistant Professor of Economics
safner@hood.edu
ryansafner/metricsf19
metricsF19.classes.ryansafner.com
Types of Data I
- Cross-sectional data: individual i
| ABCDEFGHIJ0123456789 |
state <fctr> | year <fctr> | deaths <dbl> | cell_plans <dbl> |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 2012 | 13.316056 | 9433.800 |
| Alaska | 2012 | 12.311976 | 8872.799 |
| Arizona | 2012 | 13.720419 | 8810.889 |
| Arkansas | 2012 | 16.466730 | 10047.027 |
| California | 2012 | 8.756507 | 9362.424 |
| Colorado | 2012 | 10.092204 | 9403.225 |
Types of Data I
- Cross-sectional data: individual i
| ABCDEFGHIJ0123456789 |
state <fctr> | year <fctr> | deaths <dbl> | cell_plans <dbl> |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 2012 | 13.316056 | 9433.800 |
| Alaska | 2012 | 12.311976 | 8872.799 |
| Arizona | 2012 | 13.720419 | 8810.889 |
| Arkansas | 2012 | 16.466730 | 10047.027 |
| California | 2012 | 8.756507 | 9362.424 |
| Colorado | 2012 | 10.092204 | 9403.225 |
- Time-series data: time t
| ABCDEFGHIJ0123456789 |
state <fctr> | year <fctr> | deaths <dbl> | cell_plans <dbl> |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maryland | 2007 | 10.866679 | 8942.137 |
| Maryland | 2008 | 10.740963 | 9290.689 |
| Maryland | 2009 | 9.892754 | 9339.452 |
| Maryland | 2010 | 8.783883 | 9630.120 |
| Maryland | 2011 | 8.626745 | 10335.795 |
| Maryland | 2012 | 8.941916 | 10393.295 |
Types of Data I
- Cross-sectional data: individual i
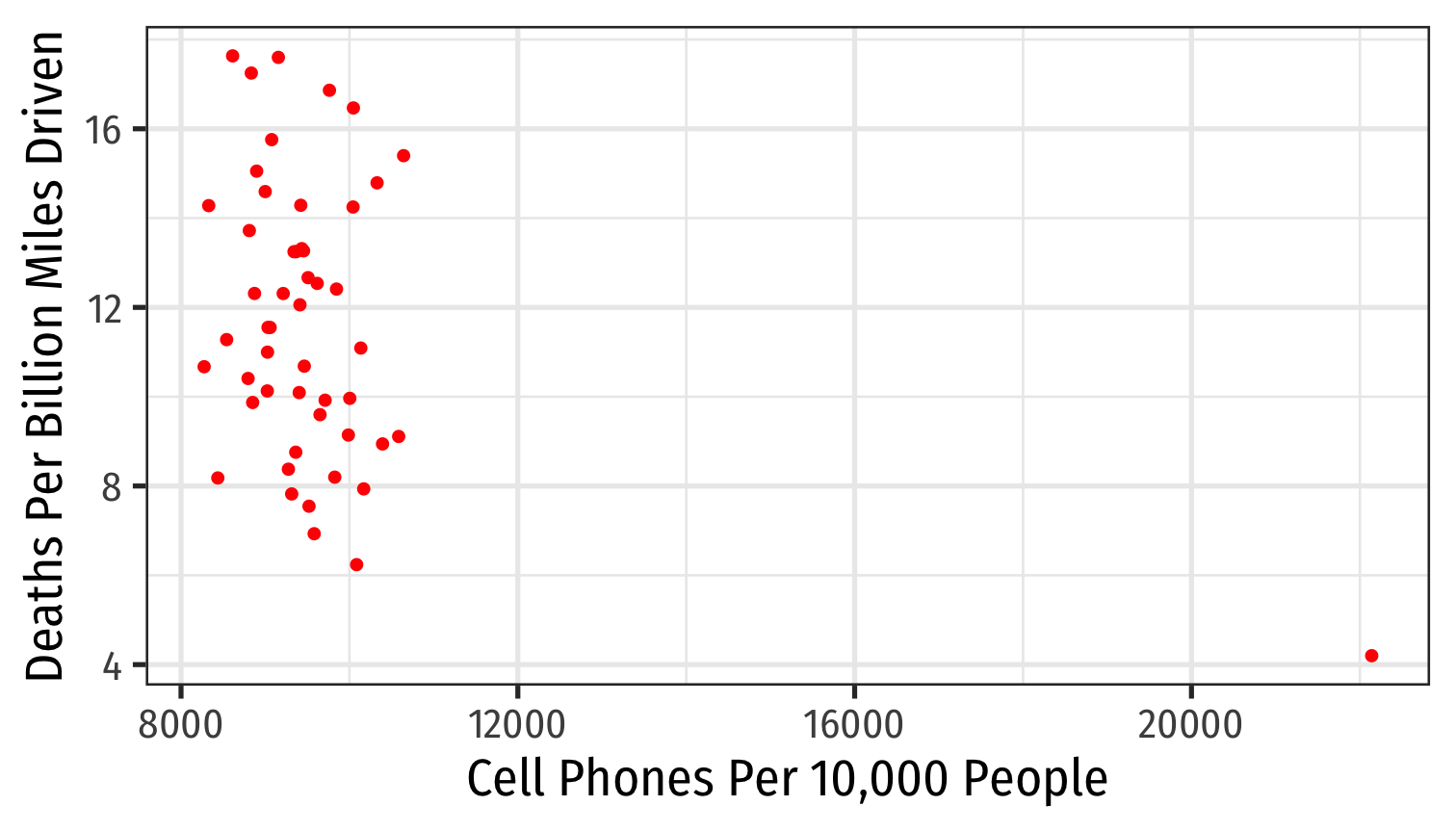
- Time-series data: time t
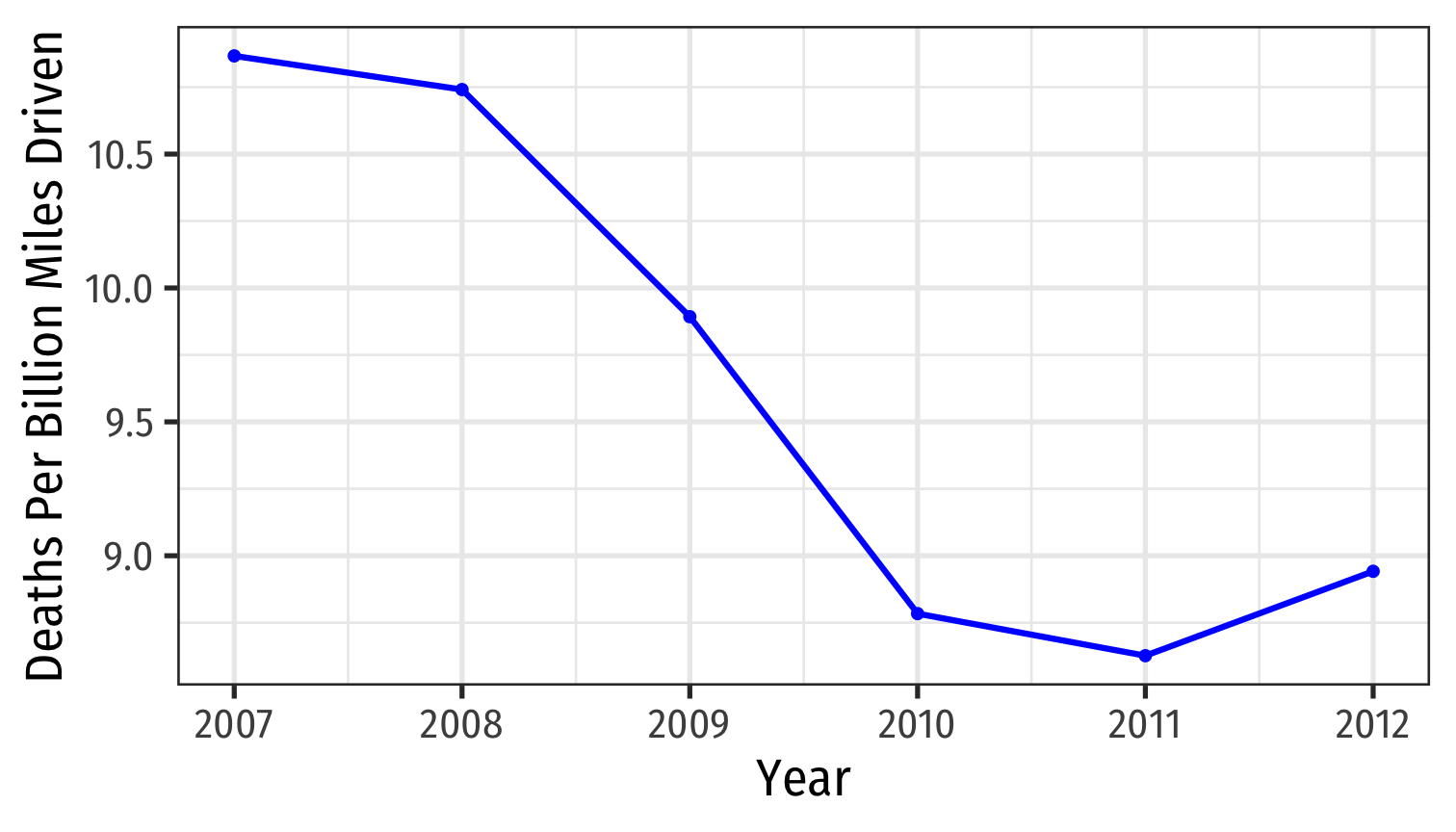
Types of Data I
- Cross-sectional data: individual i

- Time-series data: time t

- Panel data: combines these dimensions: individual i at time t
Panel Data I
Panel Data II
| ABCDEFGHIJ0123456789 |
state <fctr> | year <fctr> | deaths <dbl> | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 2007 | 18.075232 | |
| Alabama | 2008 | 16.289227 | |
| Alabama | 2009 | 13.833678 | |
| Alabama | 2010 | 13.434084 | |
| Alabama | 2011 | 13.771989 | |
| Alabama | 2012 | 13.316056 | |
| Alaska | 2007 | 16.301184 | |
| Alaska | 2008 | 12.744090 | |
| Alaska | 2009 | 12.973849 | |
| Alaska | 2010 | 11.670893 |
- Panel or Longitudinal data contains
- repeated observations (t)
- on multiple individuals (i)
Panel Data II
| ABCDEFGHIJ0123456789 |
state <fctr> | year <fctr> | deaths <dbl> | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 2007 | 18.075232 | |
| Alabama | 2008 | 16.289227 | |
| Alabama | 2009 | 13.833678 | |
| Alabama | 2010 | 13.434084 | |
| Alabama | 2011 | 13.771989 | |
| Alabama | 2012 | 13.316056 | |
| Alaska | 2007 | 16.301184 | |
| Alaska | 2008 | 12.744090 | |
| Alaska | 2009 | 12.973849 | |
| Alaska | 2010 | 11.670893 |
Panel or Longitudinal data contains
- repeated observations (t)
- on multiple individuals (i)
Thus, our regression equation looks like:
^Yit=β0+β1Xit+uit
for individual i in time t.
Panel Data: Our Motivating Example
| ABCDEFGHIJ0123456789 |
state <fctr> | year <fctr> | deaths <dbl> | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 2007 | 18.075232 | |
| Alabama | 2008 | 16.289227 | |
| Alabama | 2009 | 13.833678 | |
| Alabama | 2010 | 13.434084 | |
| Alabama | 2011 | 13.771989 | |
| Alabama | 2012 | 13.316056 | |
| Alaska | 2007 | 16.301184 | |
| Alaska | 2008 | 12.744090 | |
| Alaska | 2009 | 12.973849 | |
| Alaska | 2010 | 11.670893 |
Example: Do cell phones cause more traffic fatalities?
No measure of cell phones used while driving
cell_plansas a proxy for cell phone usage
State-level data over 6 years
The Data I
glimpse(phones)## Observations: 306## Variables: 8## $ year <fct> 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2…## $ state <fct> Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorad…## $ urban_percent <dbl> 30, 55, 45, 21, 54, 34, 84, 31, 100, 53, 39, 45, 11, 56…## $ cell_plans <dbl> 8135.525, 6730.282, 7572.465, 8071.125, 8821.933, 8162.…## $ cell_ban <fct> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0…## $ text_ban <fct> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0…## $ deaths <dbl> 18.075232, 16.301184, 16.930578, 19.595430, 12.104340, …## $ year_num <dbl> 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2…The Data II
phones %>% count(state)phones %>% count(year)| ABCDEFGHIJ0123456789 |
year <fctr> | n <int> | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 51 | |||
| 2008 | 51 | |||
| 2009 | 51 | |||
| 2010 | 51 | |||
| 2011 | 51 | |||
| 2012 | 51 |
The Data IV
phones %>% summarize(States = n_distinct(state), Years = n_distinct(year))| ABCDEFGHIJ0123456789 |
States <int> | Years <int> | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 | 6 |
The Data: With plm
# install.packages("plm")library(plm)pdim(phones, index=c("state","year"))## Balanced Panel: n = 51, T = 6, N = 306plmpackage for panel data in Rpdim()checks dimensions of panel datasetindex=vector of "group" & "year" variables
Returns with a summary of:
ngroupsTperiodsNtotal observaitons
Pooled Regression I
- What if we just ran a standard regression:
^Yit=β0+β1Xit+uit
Pooled Regression I
- What if we just ran a standard regression:
^Yit=β0+β1Xit+uit
- N number of i groups (e.g. U.S. States)
- T number of t periods (e.g. years)
- This is a pooled regression model: treats all observations as independent
Pooled Regression II
pooled<-lm(deaths~cell_plans, data=phones)summary(pooled)## ## Call:## lm(formula = deaths ~ cell_plans, data = phones)## ## Residuals:## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max ## -6.0951 -2.6411 -0.2893 2.2755 11.2665 ## ## Coefficients:## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|) ## (Intercept) 17.3371034 0.9753845 17.775 < 2e-16 ***## cell_plans -0.0005666 0.0001070 -5.297 2.26e-07 ***## ---## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1## ## Residual standard error: 3.279 on 304 degrees of freedom## Multiple R-squared: 0.0845, Adjusted R-squared: 0.08148 ## F-statistic: 28.06 on 1 and 304 DF, p-value: 2.264e-07Pooled Regression III
ggplot(data = phones)+ aes(x = cell_plans, y = deaths)+ geom_point()+ labs(x = "Cell Phones Per 10,000 People", y = "Deaths Per Billion Miles Driven")+ theme_bw(base_family = "Fira Sans Condensed", base_size=18)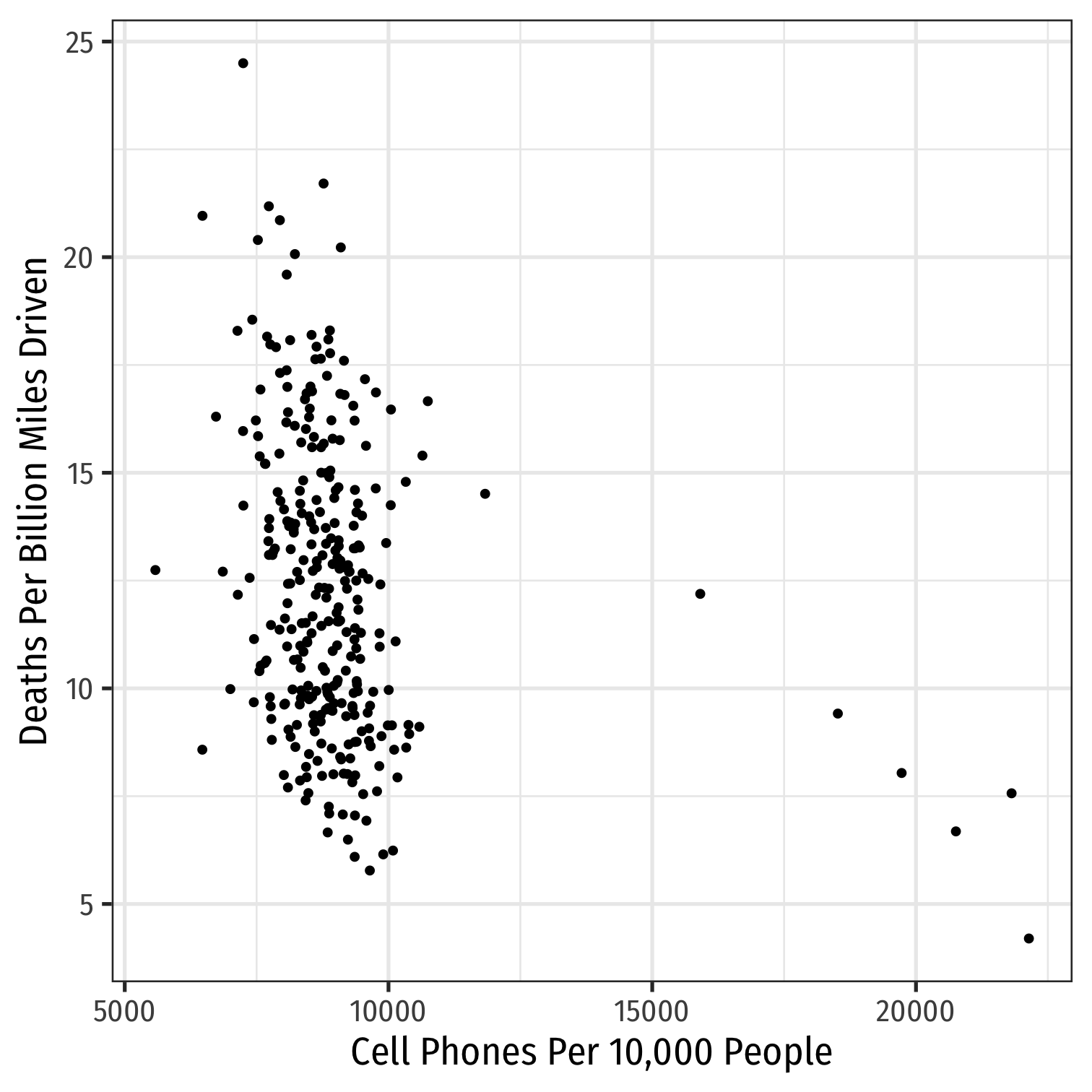
Pooled Regression III
ggplot(data = phones)+ aes(x = cell_plans, y = deaths)+ geom_point()+ geom_smooth(method = "lm", color = "red")+ labs(x = "Cell Phones Per 10,000 People", y = "Deaths Per Billion Miles Driven")+ theme_bw(base_family = "Fira Sans Condensed", base_size=18)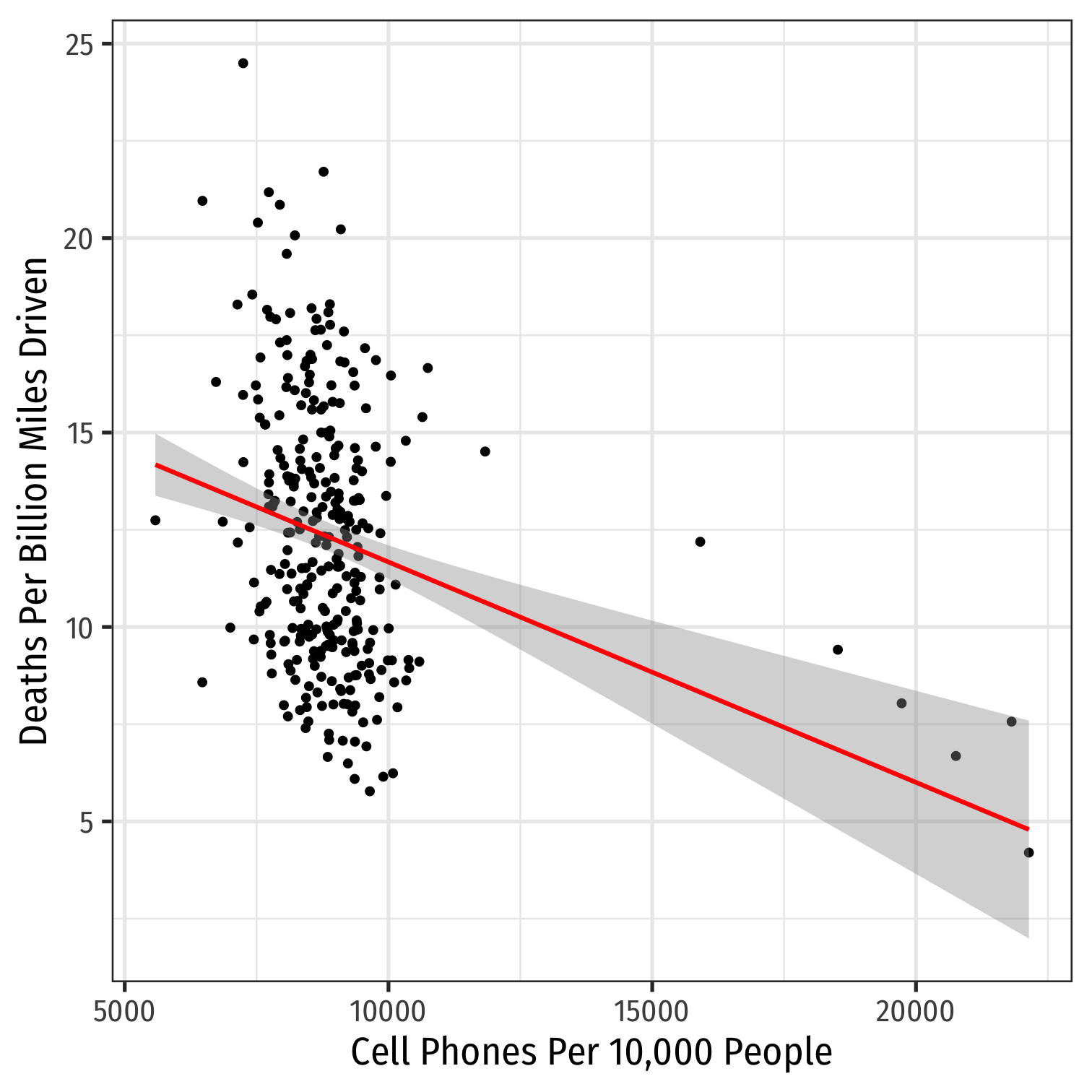
Recap: Assumptions about Errors
- Recall the 4 critical assumptions about u:
The expected value of the residuals is 0 E[u]=0
The variance of the residuals over X is constant, written: var(u|X)=σ2u
Errors are not correlated across observations: cor(ui,uj)=0∀i≠j
No correlation between X and the error term: cor(X,u)=0 or E[u|X]=0

Biases of Pooled Regression
^Yit=β0+β1Xit+ϵit
Assumption 3: cor(ui,uj)=0∀i≠j
Pooled regression model is biased because it ignores:
- Multiple observations from same group i
- Multiple observations from same time t
Thus, errors are serially or auto-correlated; cor(ui,uj)≠0 within same i and within same t
Biases of Pooled Regression: Our Example
^Deathsit=β0+β1Cell Phonesit+uit
Multiple observations from same state i
- Probably similarities among u for obs in same state
Multiple observations from same year t
- Probably similarities among u for obs in same year
Look at 5 States
phones %>% filter(state %in% c("District of Columbia", "Maryland", "Texas", "California", "Kansas")) %>%ggplot(data = .)+ aes(x = cell_plans, y = deaths)+ geom_point(aes(color = state))+ geom_smooth(method = "lm", color = "red")+ labs(x = "Cell Phones Per 10,000 People", y = "Deaths Per Billion Miles Driven", color = NULL)+ theme_bw(base_family = "Fira Sans Condensed", base_size=18)+ theme(legend.position = "top")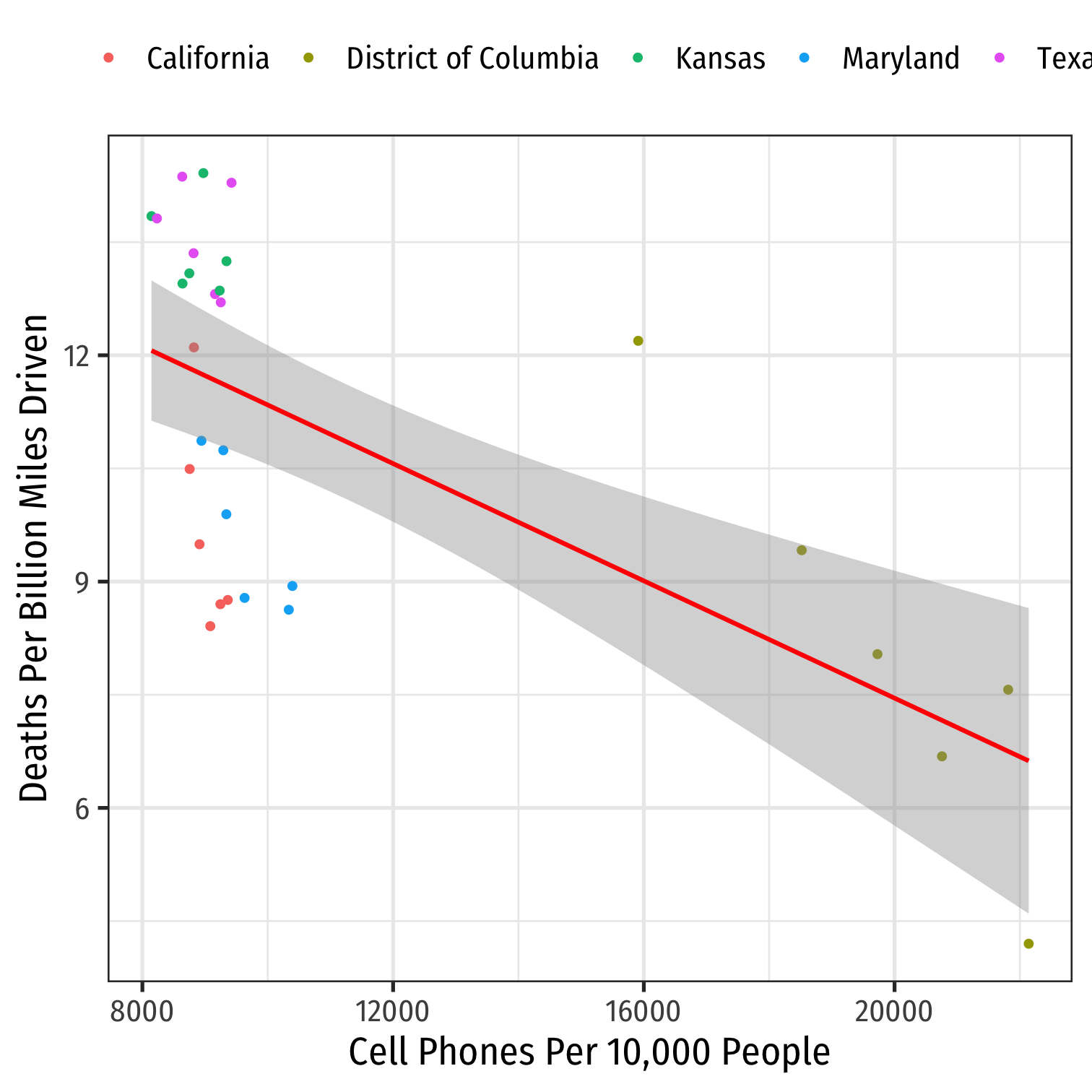
Look at 5 States
phones %>% filter(state %in% c("District of Columbia", "Maryland", "Texas", "California", "Kansas")) %>%ggplot(data = .)+ aes(x = cell_plans, y = deaths, color = state)+ geom_point()+ geom_smooth(method = "lm")+ labs(x = "Cell Phones Per 10,000 People", y = "Deaths Per Billion Miles Driven", color = NULL)+ theme_bw(base_family = "Fira Sans Condensed", base_size=18)+ theme(legend.position = "top")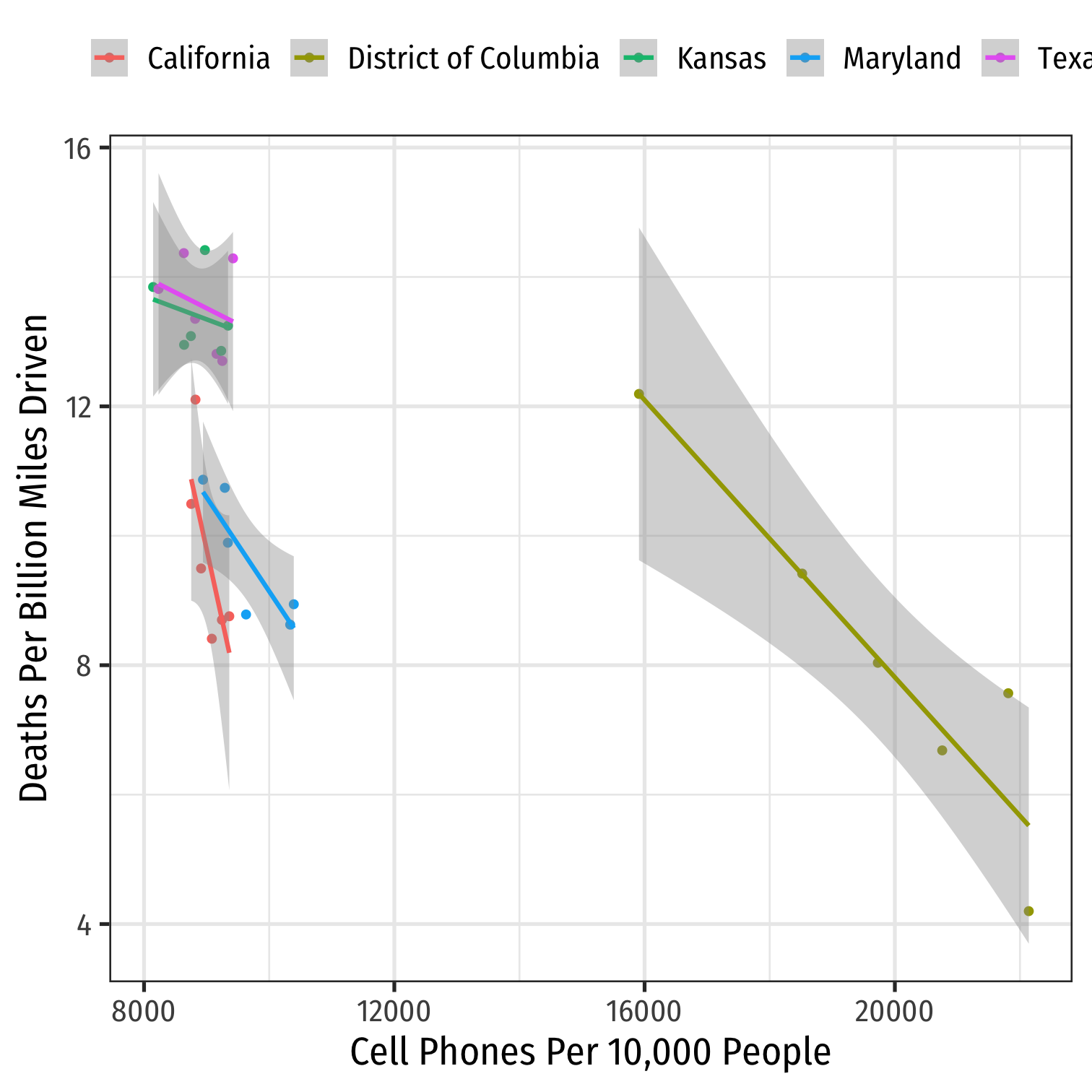
Look at 5 States
phones %>% filter(state %in% c("District of Columbia", "Maryland", "Texas", "California", "Kansas")) %>%ggplot(data = .)+ aes(x = cell_plans, y = deaths, color = state)+ geom_point()+ geom_smooth(method = "lm")+ labs(x = "Cell Phones Per 10,000 People", y = "Deaths Per Billion Miles Driven", color = NULL)+ theme_bw(base_family = "Fira Sans Condensed", base_size=18)+ theme(legend.position = "none")+ facet_wrap(~state, ncol=3)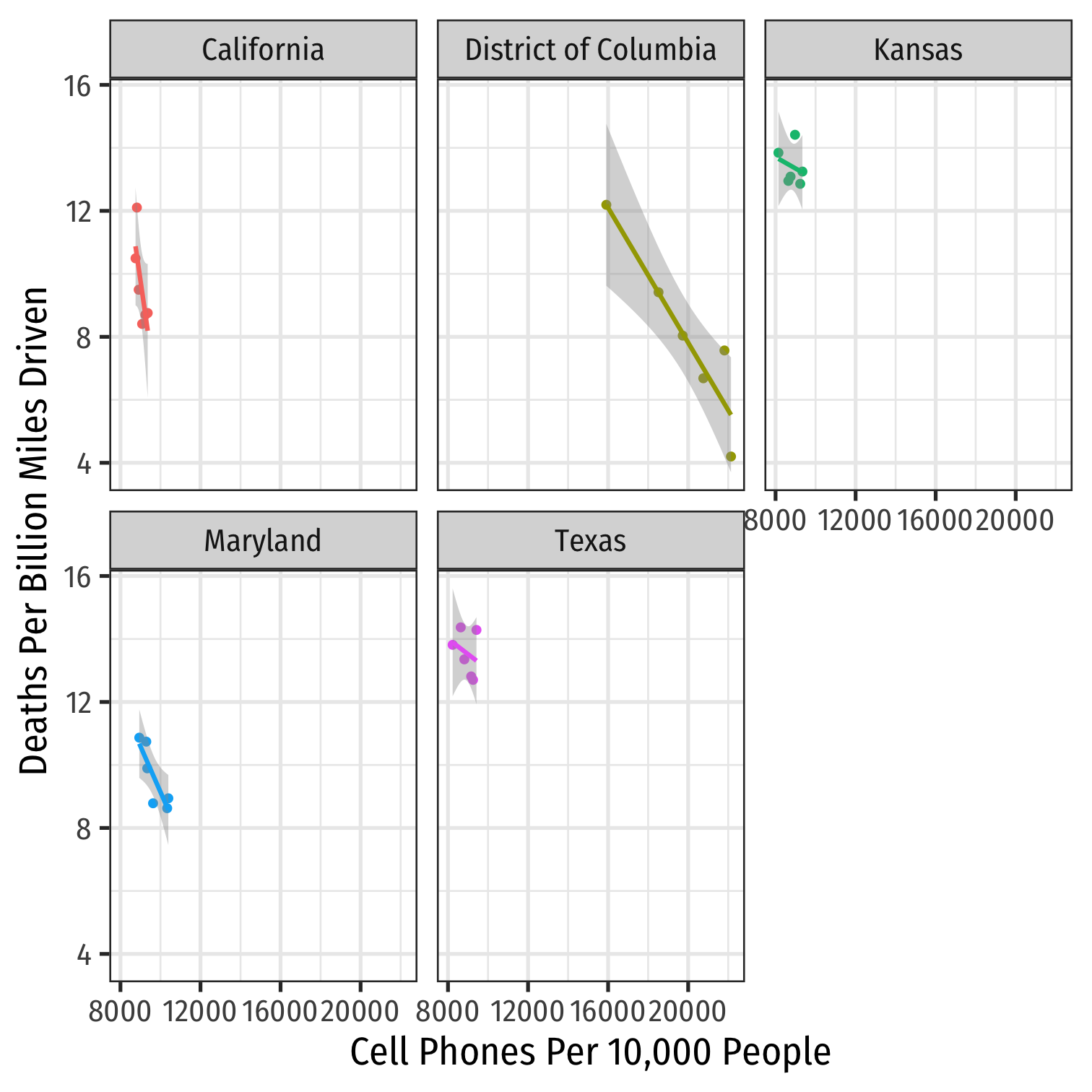
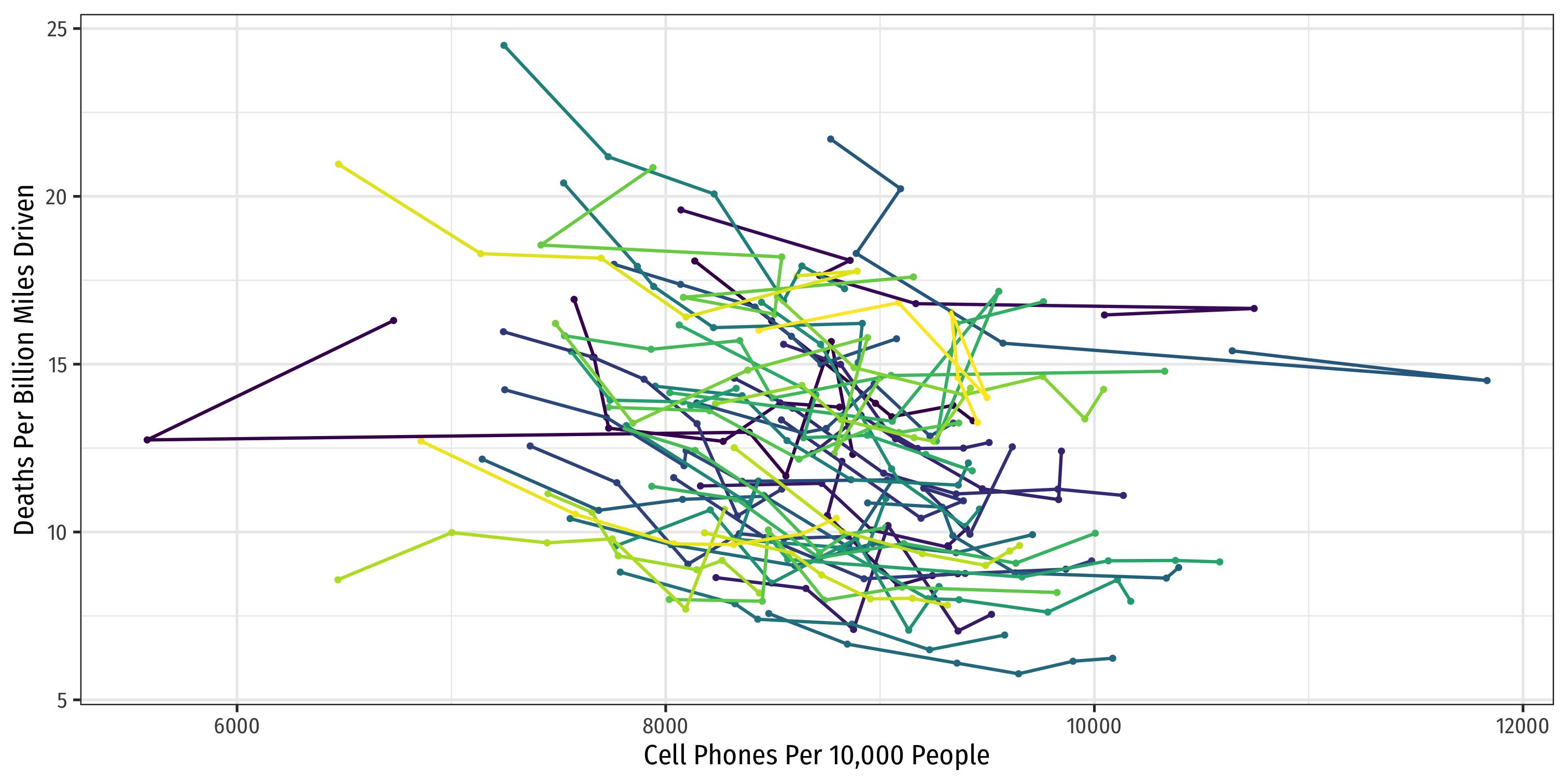
Look at All States
ggplot(data = phones)+ aes(x = cell_plans, y = deaths, color = state)+ geom_point()+ geom_smooth(method = "lm")+ labs(x = "Cell Phones Per 10,000 People", y = "Deaths Per Billion Miles Driven", color = NULL)+ theme_bw(base_family = "Fira Sans Condensed")+ theme(legend.position = "none")+ facet_wrap(~state, ncol=7)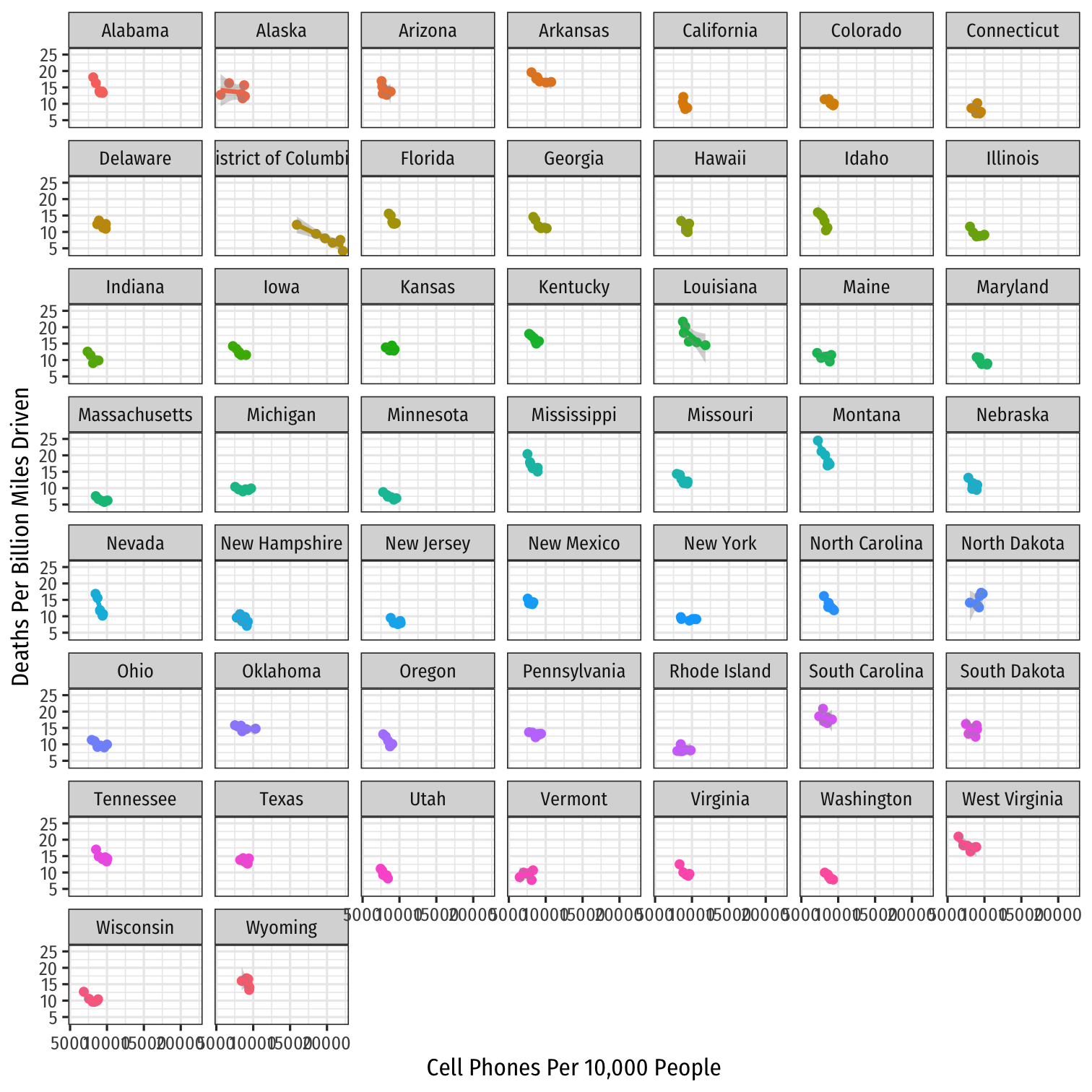
The Bias in our Pooled Regression
^Deathsit=β0+β1Cell Phonesit+uit
- Cell Phonesit is endogenous:
The Bias in our Pooled Regression
^Deathsit=β0+β1Cell Phonesit+uit
- Cell Phonesit is endogenous:
cor(uit,cell phonesit)≠0E[uit|cell phonesit]≠0
The Bias in our Pooled Regression
^Deathsit=β0+β1Cell Phonesit+uit
- Cell Phonesit is endogenous:
cor(uit,cell phonesit)≠0E[uit|cell phonesit]≠0
- Things in uit correlated with Cell phonesit:
- infrastructure spending, population, urban vs. rural, more/less cautious citizens, cultural attitudes towards driving, texting, etc
The Bias in our Pooled Regression
^Deathsit=β0+β1Cell Phonesit+uit
- Cell Phonesit is endogenous:
cor(uit,cell phonesit)≠0E[uit|cell phonesit]≠0
Things in uit correlated with Cell phonesit:
- infrastructure spending, population, urban vs. rural, more/less cautious citizens, cultural attitudes towards driving, texting, etc
A lot of these things vary systematically by State!
- cor(uit1,uit2)≠0
- Error in State i during t1 correlates with error in State i during t2 (things in State that don't change over time)
Fixed Effects Model
Fixed Effects: Decomposing uit
- Much of the endogeneity in Xit can be explained by systematic differences across i (groups)
Fixed Effects: Decomposing uit
Much of the endogeneity in Xit can be explained by systematic differences across i (groups)
Exploit the systematic variation across groups with a fixed effects model
Fixed Effects: Decomposing uit
Much of the endogeneity in Xit can be explained by systematic differences across i (groups)
Exploit the systematic variation across groups with a fixed effects model
Decompose the error term into two parts:
uit=αi+ϵit
Fixed Effects: αi
uit=αi+ϵit
αi are group-specific fixed effects
- group i tends to have higher or lower ˆY than other groups given regressor(s) Xit
- estimate a separate αi for each group i
- essentially, a separate constant (or intercept), (^β0) for each group
This includes all factors that do not change within group
(i)over time
Fixed Effects: ϵit
uit=αi+ϵit
ϵit is the remaining random error
- As usual in OLS, assume the four assumptions about this error:
- E[ϵit]=0, var[ϵit]=σ2ϵ, cor(ϵit,ϵjt)=0, cor(ϵit,Xit)=0
Includes all other factors affecting Yit not contained in group effect αi
- i.e. differences within each group that change over time
Xit can still be endogenous from non-group-specific effects!
Fixed Effects: New Regression Equation
ˆYit=β0+β1Xit+αi+ϵit
We've pulled αi out of the original error term into the regression
Essentially we'll estimate an intercept for each group (minus one, which is β0)
Must have multiple observations (over time) for each group (i.e. panel data)
Fixed Effects: Our Example
^Deathsit=β0+β1Cell phonesit+αi+ϵit
αi is the State fixed effect
- Captures everything unique about each state i that does not change over time
- culture, institutions, history, geography, climate, etc!
There could still be factors in ϵit that are correlated with Cell phonesit!
- things that do change over time within States
- Perhaps a State has a cell phone ban only for some years in our data
Estimating Fixed Effects Models
ˆYit=β0+β1Xit+αi
- Two methods to estimate fixed effects models:
Least Squares Dummy Variable (LSDV) approach
De-meaned data approach
Least Squares Dummy Variable Approach
Least Squares Dummy Variable Approach
^Yit=β0+β1Xit+β2D1i+β3D2i+⋯+βND(N−1)i
- A dummy variable Di={1 if observation is from group i0 if observation is not from group i for each possible group =1 if observation it is from group i, otherwise =0
Least Squares Dummy Variable Approach
^Yit=β0+β1Xit+β2D1i+β3D2i+⋯+βND(N−1)i
A dummy variable Di={1 if observation is from group i0 if observation is not from group i for each possible group =1 if observation it is from group i, otherwise =0
If there are N groups:
- Include N−1 dummies (to avoid dummy variable trap) and β0 is the reference category1
Least Squares Dummy Variable Approach
^Yit=β0+β1Xit+β2D1i+β3D2i+⋯+βND(N−1)i
A dummy variable Di={1 if observation is from group i0 if observation is not from group i for each possible group =1 if observation it is from group i, otherwise =0
If there are N groups:
- Include N−1 dummies (to avoid dummy variable trap) and β0 is the reference category1
So we are estimating different intercepts for each group
Least Squares Dummy Variable Approach
^Yit=β0+β1Xit+β2D1i+β3D2i+⋯+βND(N−1)i
A dummy variable Di={1 if observation is from group i0 if observation is not from group i for each possible group =1 if observation it is from group i, otherwise =0
If there are N groups:
- Include N−1 dummies (to avoid dummy variable trap) and β0 is the reference category1
So we are estimating different intercepts for each group
Sounds like a lot of work, automatic in
R
Least Squares Dummy Variable Approach
^Yit=β0+β1Xit+β2D1i+β3D2i+⋯+βND(N−1)i
A dummy variable Di={1 if observation is from group i0 if observation is not from group i for each possible group =1 if observation it is from group i, otherwise =0
If there are N groups:
- Include N−1 dummies (to avoid dummy variable trap) and β0 is the reference category1
So we are estimating different intercepts for each group
Sounds like a lot of work, automatic in
RThis soaks up anything in the error term fixed within groups over time!
1 If we do not estimate β0, we could include all N dummies. In either case, β0 takes the place of one category-dummy.
Least Squares Dummy Variable Approach: Our Example
Example: ^Deathsit=β1Cell Phonesit+Alabamai+Alaskai+⋯+Wyomingi
Our Example in R I
^Deathsit=β1Cell Phonesit+Alabamai+Alaskai+⋯+Wyomingi
If
stateis afactorvariable, just include it in the regressionRautomatically creates N−1 dummy variables and includes them in the regression- Keeps intercept and leaves out first group dummy
Our Example in R II
fe_reg_1<-lm(deaths~cell_plans+state, data = phones)summary(fe_reg_1)Our Example in R II
fe_reg_1<-lm(deaths~cell_plans+state, data = phones)summary(fe_reg_1)## ## Call:## lm(formula = deaths ~ cell_plans + state, data = phones)## ## Residuals:## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max ## -3.5617 -0.6577 -0.1353 0.5997 3.7087 ## ## Coefficients:## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|) ## (Intercept) 25.5076799 1.0176400 25.066 < 2e-16 ***## cell_plans -0.0012037 0.0001013 -11.881 < 2e-16 ***## stateAlaska -2.4841648 0.6745076 -3.683 0.000282 ***## stateArizona -1.5105774 0.6704570 -2.253 0.025109 * ## stateArkansas 3.1926629 0.6664384 4.791 2.83e-06 ***## stateCalifornia -4.9786687 0.6655468 -7.481 1.21e-12 ***## stateColorado -4.3445535 0.6654735 -6.529 3.59e-10 ***## stateConnecticut -6.5951855 0.6654429 -9.911 < 2e-16 ***## stateDelaware -2.0983936 0.6666483 -3.148 0.001842 ** ## stateDistrict of Columbia 6.3557900 1.2897173 4.928 1.50e-06 ***## stateFlorida -1.0347656 0.6656584 -1.554 0.121310 ## stateGeorgia -2.1693995 0.6661316 -3.257 0.001281 ** ## stateHawaii -2.9915131 0.6662205 -4.490 1.08e-05 ***## stateIdaho -2.4608133 0.6721521 -3.661 0.000306 ***## stateIllinois -5.0620677 0.6657586 -7.603 5.59e-13 ***## stateIndiana -5.2284659 0.6696566 -7.808 1.53e-13 ***## stateIowa -3.2495889 0.6705450 -4.846 2.19e-06 ***## stateKansas -1.4581629 0.6654571 -2.191 0.029345 * ## stateKentucky 1.0915751 0.6671138 1.636 0.103023 ## stateLouisiana 3.9178819 0.6715685 5.834 1.64e-08 ***## stateMaine -4.6283292 0.6691173 -6.917 3.73e-11 ***## stateMaryland -4.2430981 0.6697410 -6.335 1.07e-09 ***## stateMassachusetts -7.7934371 0.6672061 -11.681 < 2e-16 ***## stateMichigan -5.3689561 0.6657520 -8.064 2.91e-14 ***## stateMinnesota -7.5721267 0.6657464 -11.374 < 2e-16 ***## stateMississippi 1.5615987 0.6689602 2.334 0.020357 * ## stateMissouri -2.2813452 0.6656121 -3.427 0.000711 ***## stateMontana 4.0032162 0.6692246 5.982 7.46e-09 ***## stateNebraska -4.3224747 0.6667641 -6.483 4.66e-10 ***## stateNevada -1.8496986 0.6655435 -2.779 0.005856 ** ## stateNew Hampshire -6.1273821 0.6660296 -9.200 < 2e-16 ***## stateNew Jersey -5.7073658 0.6688922 -8.533 1.31e-15 ***## stateNew Mexico -1.7191586 0.6716722 -2.560 0.011062 * ## stateNew York -4.7548279 0.6694121 -7.103 1.23e-11 ***## stateNorth Carolina -1.5292152 0.6654724 -2.298 0.022378 * ## stateNorth Dakota 0.5958807 0.6659609 0.895 0.371758 ## stateOhio -4.6832026 0.6654475 -7.038 1.82e-11 ***## stateOklahoma -0.0654323 0.6660894 -0.098 0.921824 ## stateOregon -4.2716778 0.6667266 -6.407 7.16e-10 ***## statePennsylvania -1.9224145 0.6658671 -2.887 0.004223 ** ## stateRhode Island -6.5332075 0.6655747 -9.816 < 2e-16 ***## stateSouth Carolina 2.5662807 0.6685038 3.839 0.000156 ***## stateSouth Dakota -0.8890418 0.6673510 -1.332 0.183990 ## stateTennessee 0.5437220 0.6675007 0.815 0.416085 ## stateTexas -1.2153059 0.6654310 -1.826 0.068972 . ## stateUtah -6.3933504 0.6723736 -9.509 < 2e-16 ***## stateVermont -7.0703850 0.6803788 -10.392 < 2e-16 ***## stateVirginia -4.4686467 0.6660141 -6.710 1.26e-10 ***## stateWashington -6.2367572 0.6654881 -9.372 < 2e-16 ***## stateWest Virginia 2.1062917 0.6744981 3.123 0.001999 ** ## stateWisconsin -5.3569895 0.6712323 -7.981 5.02e-14 ***## stateWyoming 0.7736131 0.6660728 1.161 0.246547 ## ---## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1## ## Residual standard error: 1.153 on 254 degrees of freedom## Multiple R-squared: 0.9055, Adjusted R-squared: 0.8865 ## F-statistic: 47.72 on 51 and 254 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16Our Example in R II
| ABCDEFGHIJ0123456789 |
term <chr> | estimate <dbl> | std.error <dbl> | statistic <dbl> | p.value <dbl> |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 25.507679925 | 1.0176400289 | 25.06552337 | 1.241581e-70 |
| cell_plans | -0.001203742 | 0.0001013125 | -11.88147584 | 3.483442e-26 |
| stateAlaska | -2.484164783 | 0.6745076282 | -3.68293060 | 2.816972e-04 |
| stateArizona | -1.510577383 | 0.6704569688 | -2.25305643 | 2.510925e-02 |
| stateArkansas | 3.192662931 | 0.6664383936 | 4.79063476 | 2.829319e-06 |
| stateCalifornia | -4.978668651 | 0.6655467951 | -7.48056889 | 1.206933e-12 |
| stateColorado | -4.344553493 | 0.6654735335 | -6.52851432 | 3.588784e-10 |
| stateConnecticut | -6.595185530 | 0.6654428902 | -9.91097152 | 8.698802e-20 |
| stateDelaware | -2.098393628 | 0.6666483193 | -3.14767707 | 1.842218e-03 |
| stateDistrict of Columbia | 6.355790010 | 1.2897172620 | 4.92804911 | 1.499627e-06 |
De-meaned Approach
De-meaned Approach I
Alternatively, we can hold group fixed effects constant without directly estimating them
We simply de-mean the data for each group
For each group i, find the means (over time, t): ˉYi=β0+β1ˉXi+ˉαi+ˉϵi
- ˉYi: average value of Yit for group i
- ˉXi: average value of Xit for group i
- ˉαi: average value of αi for group i ($=\alpha_i$)
- ˉϵi=0, by assumption
De-meaned Approach II
^Yit=β0+β1Xit+uitˉYi=β0+β1ˉXi+ˉαi+ˉϵi
- Subtract the means equation from the pooled equation to get:
Yi−ˉYi=β1(Xit−ˉXi)+˜ϵit˜Yit=β1˜Xit+˜ϵit
Within each group i, the de-meaned variables ˜Yit and ˜Xit's all have a mean of 01
Variables that don't change over time will drop out of analysis altogether
Removes any source of variation across groups to only work with variation within each group
1 Recall Rule 4 from the class notes on the Summation Operator: (\sum(X_i-\bar{X})=0)
De-meaned Approach III
˜Yit=β1˜Xit+˜ϵit
Yields identical results to dummy variable approach
More useful when we have many groups (would be many dummies)
Demonstrates intuition behind fixed effects:
- Converts all data to deviations from the mean of each group
- All groups are "centered" at 0
- Fixed effects are often called the "within" estimators, they exploit variation within groups, not across groups
De-meaned Approach IV
We are basically comparing groups to themselves over time
- apples to apples comparison
- e.g. Maryland in 2000 vs. Maryland in 2005
Ignore all differences between groups, only look at differences within groups over time
De-Meaning the Data in R I
# get means of Y and X by statemeans_state<-phones %>% group_by(state) %>% summarize(avg_deaths = mean(deaths), avg_phones = mean(cell_plans))# look at itmeans_stateDe-Meaning the Data in R I
# get means of Y and X by statemeans_state<-phones %>% group_by(state) %>% summarize(avg_deaths = mean(deaths), avg_phones = mean(cell_plans))# look at itmeans_stateDe-Meaning the Data in R II
ggplot(data = means_state)+ aes(x = fct_reorder(state,avg_deaths), y = avg_deaths, color = state)+ geom_point()+ geom_segment(aes(y=0, yend=avg_deaths, x=state, xend=state))+ coord_flip()+ labs(x = "Cell Phones Per 10,000 People", y = "Deaths Per Billion Miles Driven", color = NULL)+ theme_bw(base_family = "Fira Sans Condensed", base_size=10)+ theme(legend.position = "none")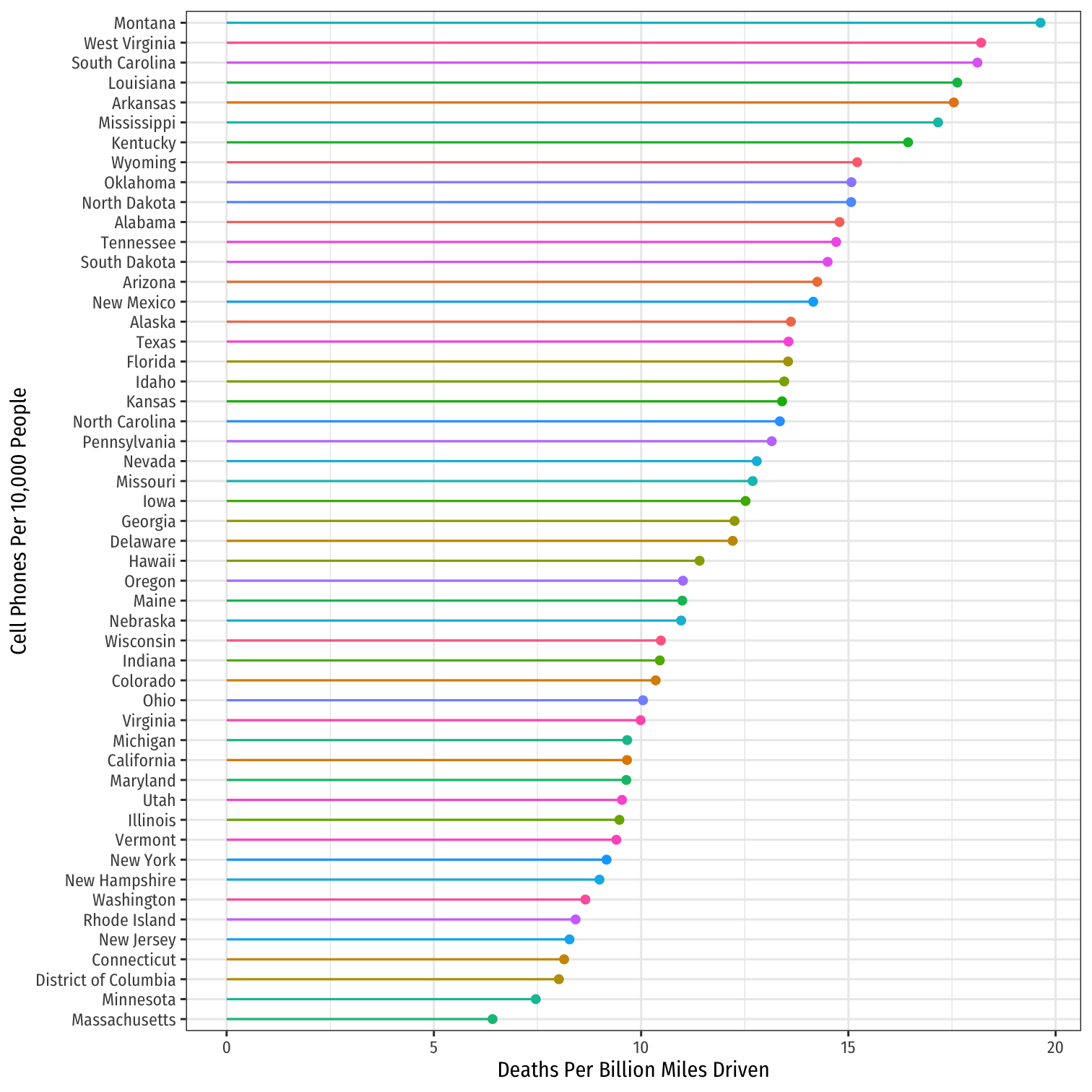
Visualizing "Within Estimates" for the 5 States
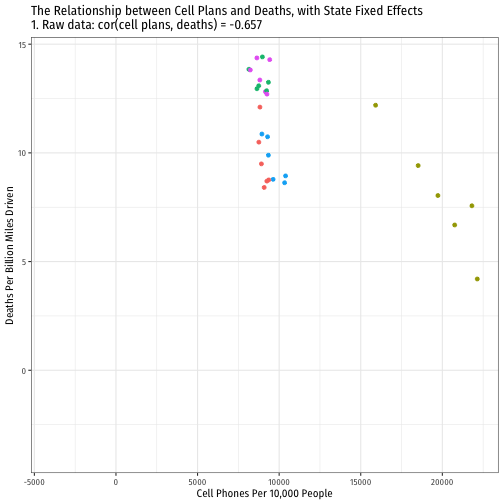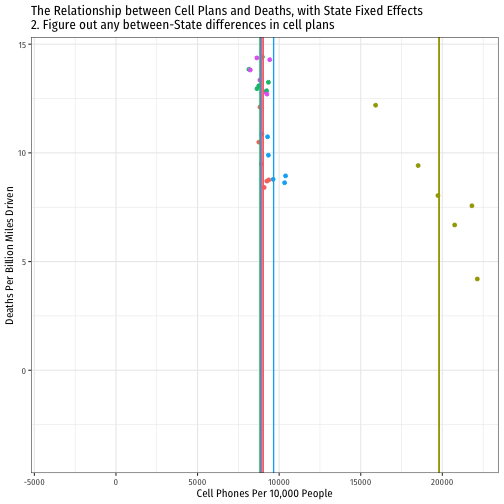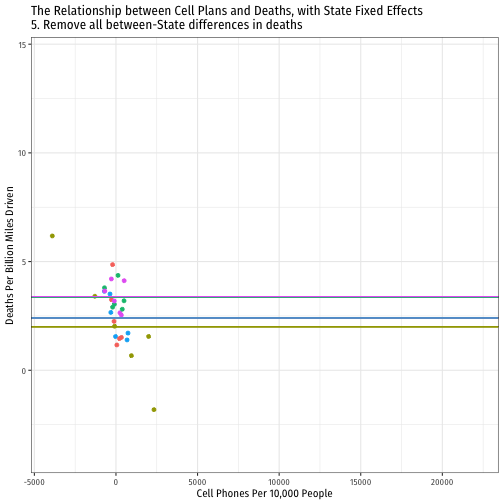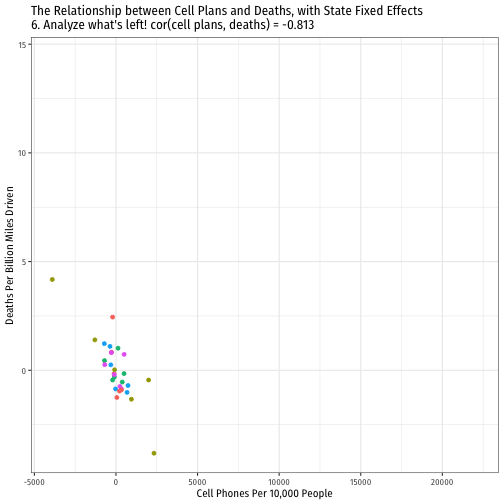
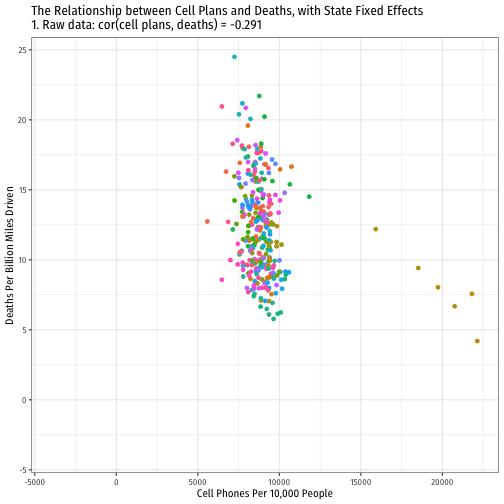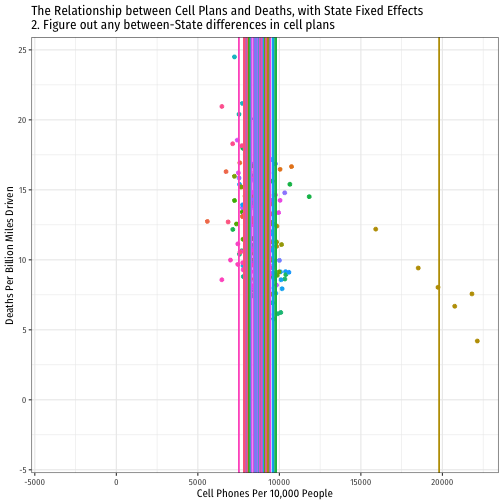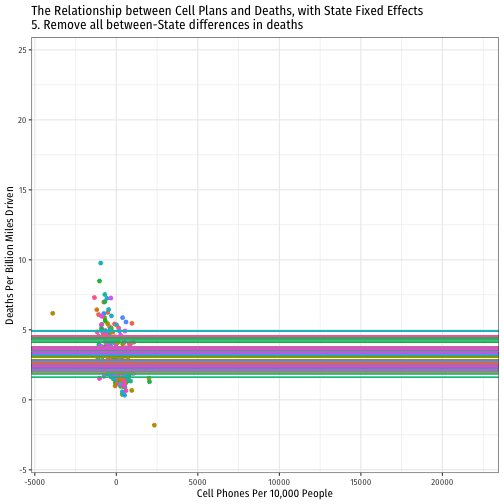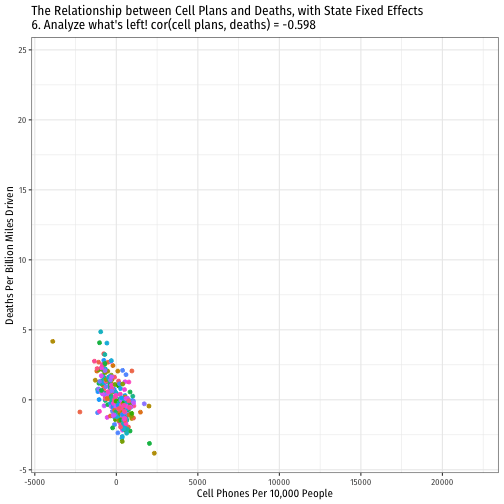
Visualizing "Within Estimates" for All 51 States
De-meaned Approach in R I
The
plmpackage is designed for panel dataplm()function is just likelm(), with some additional arguments:index="group_variable_name"set equal to the name of yourfactorvariable for the groupsmodel=set equal to"within"to use fixed-effects (within-estimator)
#install.packages("plm")library(plm)fe_reg_1_alt<-plm(deaths ~ cell_plans, data = phones, index = "state", model = "within")De-meaned Approach in R II
summary(fe_reg_1_alt)## Oneway (individual) effect Within Model## ## Call:## plm(formula = deaths ~ cell_plans, data = phones, model = "within", ## index = "state")## ## Balanced Panel: n = 51, T = 6, N = 306## ## Residuals:## Min. 1st Qu. Median 3rd Qu. Max. ## -3.56170 -0.65772 -0.13533 0.59971 3.70868 ## ## Coefficients:## Estimate Std. Error t-value Pr(>|t|) ## cell_plans -0.00120374 0.00010131 -11.882 < 2.2e-16 ***## ---## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1## ## Total Sum of Squares: 524.94## Residual Sum of Squares: 337.41## R-Squared: 0.35724## Adj. R-Squared: 0.22818## F-statistic: 141.169 on 1 and 254 DF, p-value: < 2.22e-16Two-Way Fixed Effects:
Two-Way Fixed Effects
- So far, we've looked at a one-way fixed effects model that estimates a fixed effect for groups
Two-Way Fixed Effects
So far, we've looked at a one-way fixed effects model that estimates a fixed effect for groups
Two-way fixed effects model estimates a fixed effect for both the groups and the time periods ^Yit=β0+β1Xit+αi+θt+νit
αi: group fixed effects
- accounts for time-invariant differences across groups
θt: time fixed effects
- acounts for group-invariant differences over time
Two-Way Fixed Effects: Our Example
^Deathsit=β0+β1Cell phonesit+αi+θt+ϵit
αi: State fixed effects
- differences across states that are stable over time
- e.g. geography, culture, (unchanging) state laws
θt: Year fixed effects
- differences over time that are stable across states
- e.g. economy-wide macroeconomic changes, federal laws passed
Visualizing Year Effects I
# find averages for yearsmeans_year<-phones %>% group_by(year) %>% summarize(avg_deaths = mean(deaths), avg_phones = mean(cell_plans))means_year| ABCDEFGHIJ0123456789 |
year <fctr> | avg_deaths <dbl> | avg_phones <dbl> | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 14.00751 | 8064.531 | ||
| 2008 | 12.87156 | 8482.903 | ||
| 2009 | 12.08632 | 8859.706 | ||
| 2010 | 11.61487 | 9134.592 | ||
| 2011 | 11.36431 | 9485.238 | ||
| 2012 | 11.65666 | 9660.474 |
Visualizing Year Effects II
ggplot(data = means_year)+ aes(x = year, y = avg_deaths)+ geom_point(data = phones, aes(x = year, y = deaths, color = year))+ geom_point(size=3)+ geom_path()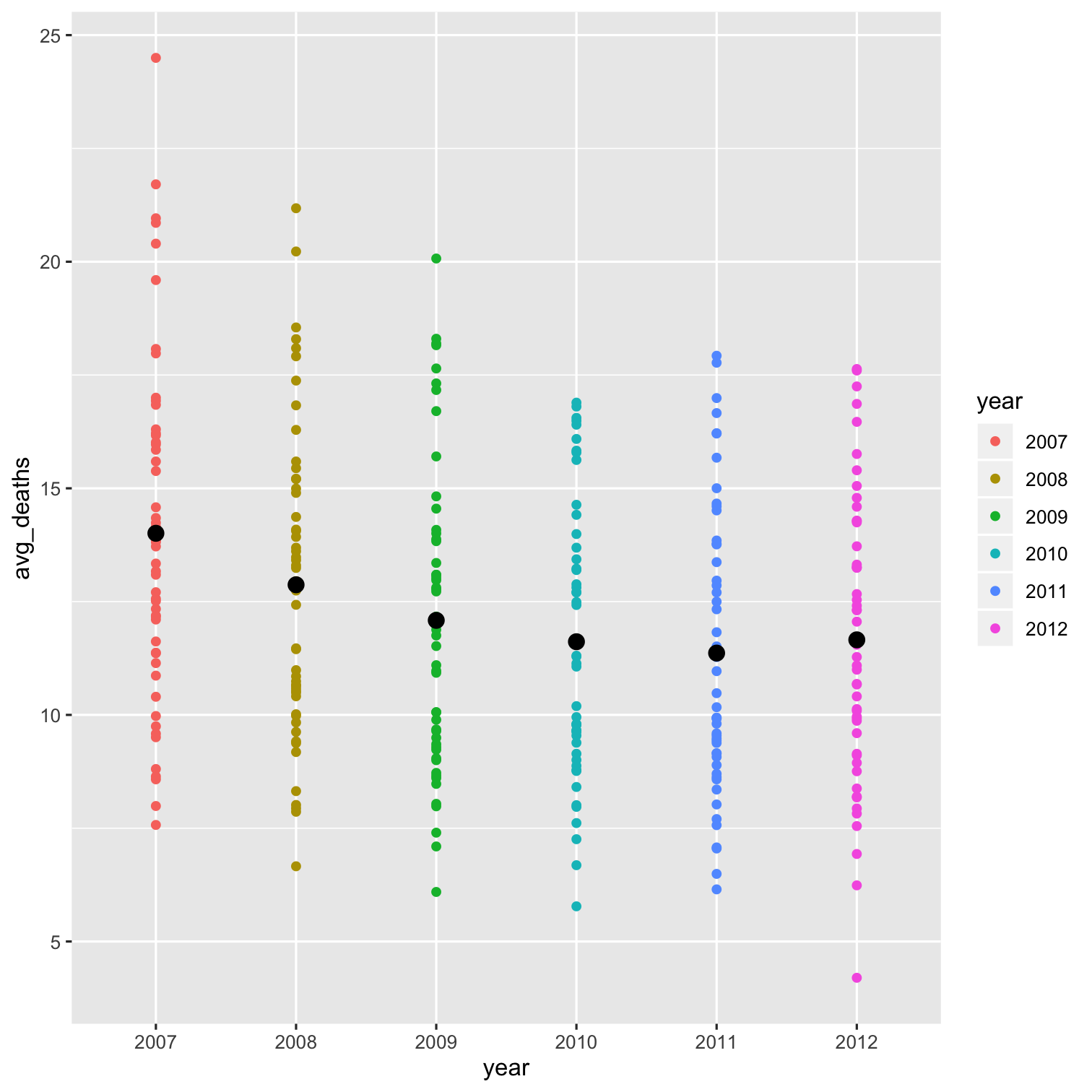
Estimating Two-Way Fixed Effects
ˆYit=β0+β1Xit+αi+θt
- As before, several equivalent ways to estimate two-way fixed effects models:
- Least Squares Dummy Variable (LSDV) Approach: add dummies for both groups and time periods (separate intercepts for groups and times)
Estimating Two-Way Fixed Effects
ˆYit=β0+β1Xit+αi+θt
- As before, several equivalent ways to estimate two-way fixed effects models:
Least Squares Dummy Variable (LSDV) Approach: add dummies for both groups and time periods (separate intercepts for groups and times)
Fully De-meaned data: ˜Yit=β1˜Xit+˜νit
where each ~variableit=variableit−¯variablet−¯variablei
Estimating Two-Way Fixed Effects
ˆYit=β0+β1Xit+αi+θt
- As before, several equivalent ways to estimate two-way fixed effects models:
Least Squares Dummy Variable (LSDV) Approach: add dummies for both groups and time periods (separate intercepts for groups and times)
Fully De-meaned data: ˜Yit=β1˜Xit+˜νit
where each ~variableit=variableit−¯variablet−¯variablei
- Hybrid: de-mean for one effect (groups or times) and add dummies for the other effect (times or groups)
LSDV Method
fe2_reg_1<-lm(deaths~cell_plans+state+year, data = phones)summary(fe2_reg_1)LSDV Method
fe2_reg_1<-lm(deaths~cell_plans+state+year, data = phones)summary(fe2_reg_1)## ## Call:## lm(formula = deaths ~ cell_plans + state + year, data = phones)## ## Residuals:## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max ## -2.7361 -0.5110 -0.0242 0.5182 3.0994 ## ## Coefficients:## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|) ## (Intercept) 18.9304707 1.4511324 13.045 < 2e-16 ***## cell_plans -0.0002995 0.0001723 -1.738 0.083400 . ## stateAlaska -1.4998292 0.6241083 -2.403 0.016986 * ## stateArizona -0.7791715 0.6113519 -1.275 0.203672 ## stateArkansas 2.8655345 0.5985063 4.788 2.90e-06 ***## stateCalifornia -5.0900897 0.5956293 -8.546 1.30e-15 ***## stateColorado -4.4127242 0.5953925 -7.411 1.95e-12 ***## stateConnecticut -6.6325835 0.5952934 -11.142 < 2e-16 ***## stateDelaware -2.4579830 0.5991822 -4.102 5.55e-05 ***## stateDistrict of Columbia -3.5044964 1.9710939 -1.778 0.076633 . ## stateFlorida -1.1904908 0.5959900 -1.998 0.046859 * ## stateGeorgia -2.4422504 0.5975175 -4.087 5.89e-05 ***## stateHawaii -3.2811475 0.5978043 -5.489 9.96e-08 ***## stateIdaho -1.6145030 0.6167130 -2.618 0.009389 ** ## stateIllinois -5.2488047 0.5963135 -8.802 2.30e-16 ***## stateIndiana -4.5580058 0.6088090 -7.487 1.22e-12 ***## stateIowa -2.5117858 0.6116310 -4.107 5.45e-05 ***## stateKansas -1.4042964 0.5953392 -2.359 0.019106 * ## stateKentucky 1.5143772 0.6006792 2.521 0.012324 * ## stateLouisiana 3.1093174 0.6148710 5.057 8.27e-07 ***## stateMaine -4.0022270 0.6070912 -6.592 2.57e-10 ***## stateMaryland -4.9202431 0.6090776 -8.078 2.84e-14 ***## stateMassachusetts -8.2276855 0.6009756 -13.691 < 2e-16 ***## stateMichigan -5.1840812 0.5962925 -8.694 4.80e-16 ***## stateMinnesota -7.3888658 0.5962744 -12.392 < 2e-16 ***## stateMississippi 2.1741873 0.6065903 3.584 0.000407 ***## stateMissouri -2.1422872 0.5958403 -3.595 0.000390 ***## stateMontana 4.6383935 0.6074334 7.636 4.80e-13 ***## stateNebraska -3.9461735 0.5995548 -6.582 2.73e-10 ***## stateNevada -1.9595530 0.5956188 -3.290 0.001147 ** ## stateNew Hampshire -5.8751509 0.5971883 -9.838 < 2e-16 ***## stateNew Jersey -6.3140122 0.6063734 -10.413 < 2e-16 ***## stateNew Mexico -0.9037640 0.6151985 -1.469 0.143079 ## stateNew York -5.4055532 0.6080308 -8.890 < 2e-16 ***## stateNorth Carolina -1.4618984 0.5953890 -2.455 0.014758 * ## stateNorth Dakota 0.3585402 0.5969666 0.601 0.548650 ## stateOhio -4.7265870 0.5953082 -7.940 6.95e-14 ***## stateOklahoma 0.1990835 0.5973813 0.333 0.739218 ## stateOregon -3.9007021 0.5994343 -6.507 4.17e-10 ***## statePennsylvania -1.7070557 0.5966639 -2.861 0.004582 ** ## stateRhode Island -6.4092098 0.5957196 -10.759 < 2e-16 ***## stateSouth Carolina 3.1378079 0.6051330 5.185 4.47e-07 ***## stateSouth Dakota -0.4374085 0.6014408 -0.727 0.467745 ## stateTennessee 0.0748011 0.6019211 0.124 0.901201 ## stateTexas -1.2268813 0.5952548 -2.061 0.040332 * ## stateUtah -5.5331389 0.6174110 -8.962 < 2e-16 ***## stateVermont -5.8044650 0.6422793 -9.037 < 2e-16 ***## stateVirginia -4.7176009 0.5971384 -7.900 8.95e-14 ***## stateWashington -6.1580557 0.5954397 -10.342 < 2e-16 ***## stateWest Virginia 3.0901095 0.6240787 4.951 1.36e-06 ***## stateWisconsin -4.5709779 0.6138081 -7.447 1.56e-12 ***## stateWyoming 0.5124453 0.5973278 0.858 0.391775 ## year2008 -1.0106325 0.2165233 -4.668 4.98e-06 ***## year2009 -1.6830082 0.2458856 -6.845 5.93e-11 ***## year2010 -2.0721270 0.2751070 -7.532 9.20e-13 ***## year2011 -2.2176559 0.3187735 -6.957 3.06e-11 ***## year2012 -1.8728162 0.3425095 -5.468 1.11e-07 ***## ---## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1## ## Residual standard error: 1.031 on 249 degrees of freedom## Multiple R-squared: 0.9259, Adjusted R-squared: 0.9092 ## F-statistic: 55.53 on 56 and 249 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16With plm
fe2_reg_2<-plm(deaths~cell_plans, index=c("state", "year"), model="within", data = phones)summary(fe2_reg_2)With plm
fe2_reg_2<-plm(deaths~cell_plans, index=c("state", "year"), model="within", data = phones)summary(fe2_reg_2)plm()command allows for multiple effects to be fit insideindex=c("group", "time")
## Oneway (individual) effect Within Model## ## Call:## plm(formula = deaths ~ cell_plans, data = phones, model = "within", ## index = c("state", "year"))## ## Balanced Panel: n = 51, T = 6, N = 306## ## Residuals:## Min. 1st Qu. Median 3rd Qu. Max. ## -3.56170 -0.65772 -0.13533 0.59971 3.70868 ## ## Coefficients:## Estimate Std. Error t-value Pr(>|t|) ## cell_plans -0.00120374 0.00010131 -11.882 < 2.2e-16 ***## ---## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1## ## Total Sum of Squares: 524.94## Residual Sum of Squares: 337.41## R-Squared: 0.35724## Adj. R-Squared: 0.22818## F-statistic: 141.169 on 1 and 254 DF, p-value: < 2.22e-16## Oneway (individual) effect Within Model## ## Call:## plm(formula = deaths ~ cell_plans, data = phones, model = "within", ## index = c("state", "year"))## ## Balanced Panel: n = 51, T = 6, N = 306## ## Residuals:## Min. 1st Qu. Median 3rd Qu. Max. ## -3.56170 -0.65772 -0.13533 0.59971 3.70868 ## ## Coefficients:## Estimate Std. Error t-value Pr(>|t|) ## cell_plans -0.00120374 0.00010131 -11.882 < 2.2e-16 ***## ---## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1## ## Total Sum of Squares: 524.94## Residual Sum of Squares: 337.41## R-Squared: 0.35724## Adj. R-Squared: 0.22818## F-statistic: 141.169 on 1 and 254 DF, p-value: < 2.22e-16Adding Covariates I
- Can still add covariates to remove endogeneity not soaked up by fixed effects
- Factors that change within groups over time
- e.g. some states pass bans over the time period in data (some years before, some years after)
^Deathsit=β1Cell Phonesit+αi+θt+urban pctit+cell banit+text banit
Adding Covariates II
fe2_controls_reg<-plm(deaths~cell_plans+text_ban+urban_percent+cell_ban, data=phones,index=c("state","year"), model="within", effect="twoways") summary(fe2_controls_reg)## Twoways effects Within Model## ## Call:## plm(formula = deaths ~ cell_plans + text_ban + urban_percent + ## cell_ban, data = phones, effect = "twoways", model = "within", ## index = c("state", "year"))## ## Balanced Panel: n = 51, T = 6, N = 306## ## Residuals:## Min. 1st Qu. Median 3rd Qu. Max. ## -2.73515 -0.51252 -0.01354 0.47735 3.14133 ## ## Coefficients:## Estimate Std. Error t-value Pr(>|t|) ## cell_plans -0.00034037 0.00017294 -1.9682 0.05017 .## text_ban1 0.25592616 0.22219230 1.1518 0.25051 ## urban_percent 0.01313477 0.01119861 1.1729 0.24197 ## cell_ban1 -0.67979565 0.40294912 -1.6871 0.09286 .## ---## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1## ## Total Sum of Squares: 267.89## Residual Sum of Squares: 259.07## R-Squared: 0.032939## Adj. R-Squared: -0.199## F-statistic: 2.09472 on 4 and 246 DF, p-value: 0.082085Comparing Models
library(huxtable)huxreg("Pooled" = pooled, "State Effects" = fe_reg_1, "State and Year Effects" = fe2_reg_1, "With Controls" = fe2_controls_reg, coefs = c("Intercept" = "(Intercept)", "Cell phones" = "cell_plans", "Cell Ban" = "cell_ban1", "Texting Ban" = "text_ban1", "Urbanization Rate" = "urban_percent"), statistics = c("N" = "nobs", "R-Squared" = "r.squared", "SER" = "sigma"), number_format = 4)Comparing Models
| Pooled | State Effects | State and Year Effects | With Controls | |
| Intercept | 17.3371 *** | 25.5077 *** | 18.9305 *** | |
| (0.9754) | (1.0176) | (1.4511) | ||
| Cell phones | -0.0006 *** | -0.0012 *** | -0.0003 | -0.0003 |
| (0.0001) | (0.0001) | (0.0002) | (0.0002) | |
| Cell Ban | -0.6798 | |||
| (0.4029) | ||||
| Texting Ban | 0.2559 | |||
| (0.2222) | ||||
| Urbanization Rate | 0.0131 | |||
| (0.0112) | ||||
| N | 306 | 306 | 306 | 306 |
| R-Squared | 0.0845 | 0.9055 | 0.9259 | 0.0329 |
| SER | 3.2791 | 1.1526 | 1.0310 | |
| *** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05. | ||||